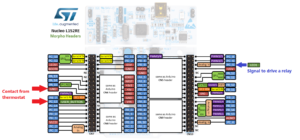
Cars are undeniably getting smarter, but few people understand why, and even fewer have a grasp on how to make them smarter as ST does.
This is because ST has been developing telematics solutions for years, long before anyone talked about autonomous driving or smart vehicles.
In keeping with that trend, ST released Telemaco3, a new family of single-chip telematics processors.
However, before one can fully grasp the power and engineering that went into these new chips, we must first understand what telematics is.
Telematics is a compound word combining “telecommunications” and “infomatics”, the science of information systems.
Hence, according to its strictly academic definition, telematics is the science of sending, receiving and storing information using a telecommunication standard.
First coined in France in 1978, the word mostly refers today to vehicle telematics, meaning the information is about a mode of transportation (boat, car, train, plane, etc.).
Furthermore, although this was not the case at first, telematics now always includes information from global navigation systems (such as the GPS) and increasingly implies the ability to remotely control a vehicle or influence its operation.
More info regarding: Driving Car Security Into the 21st Century, are here.